What are the specifications of inert ceramic balls?
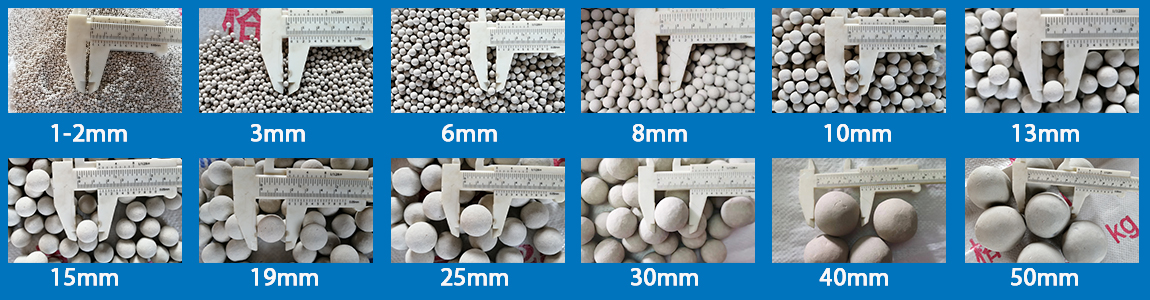
Inert ceramic ball specifications Common specifications are:
3 mm (1/8 "), 6 mm (1/4 "), 13 mm (1/2 "), 19 mm (3/4 "), 25 mm (1 "), 38 mm (1.5 ").
50mm (2 "), of course, as a manufacturer, we are custom diameter production of various inert ceramic ball specifications
Smaller diameter specifications: 3mm, 6mm, 8mm, 10mm, 12mm, etc., such small size inert ceramic balls are often used in reactors or towers with high space and distribution requirements, such as in some small experimental devices or equipment with high material distribution accuracy requirements, small diameter porcelain balls can be more evenly distributed around the catalyst, playing a good support and coverage role.

Medium diameter ceramic ball specifications: 13mm, 15mm, 20mm, 25mm, etc., which is the more commonly used specification range, suitable for most conventional chemical, petroleum and other industrial reaction units. In these devices, they can effectively support the catalyst, ensure the smooth progress of the reaction, and can better adapt to the size of the equipment and process requirements.
Larger diameter specifications: 40mm, 50mm, 60mm and above, large diameter inert ceramic balls are generally used for large industrial reactors or occasions with high support strength requirements. Due to its larger size, it can provide stronger support and can withstand greater pressure and weight, while also helping to better disperse gases or liquids in large equipment and improve reaction conditions.
In practical applications, the selection of inert ceramic ball specifications need to be considered according to the specific process requirements, equipment size, catalyst characteristics and other factors.
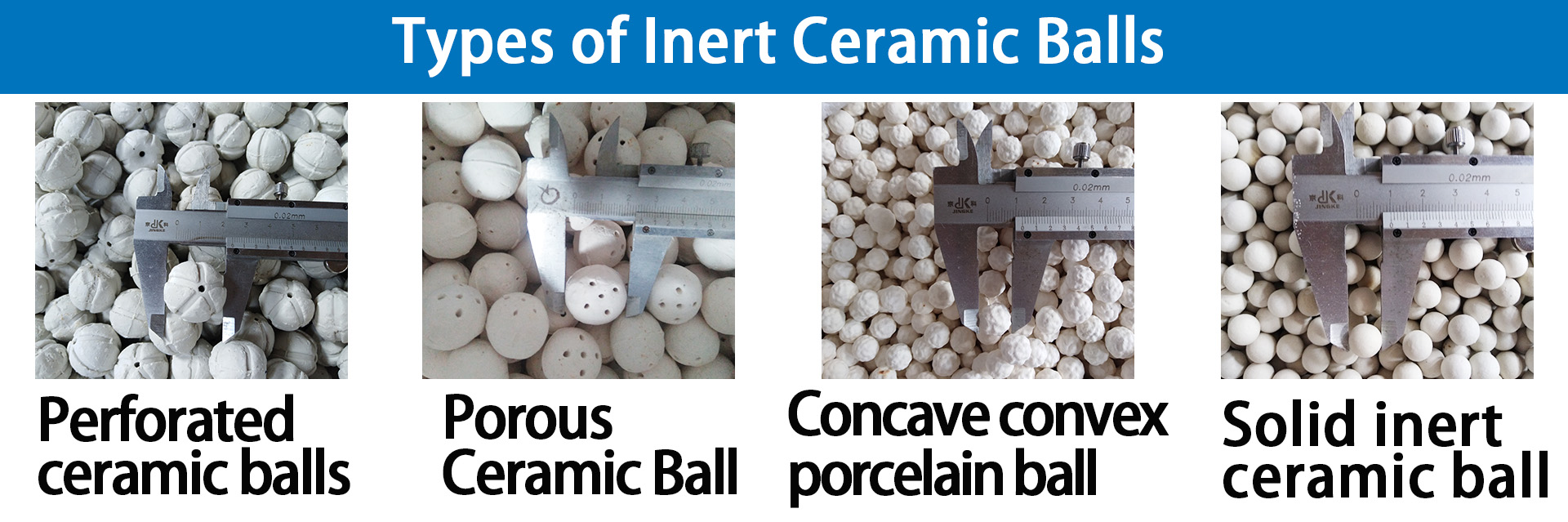
According to the process requirements, the selection of inert ceramic ball specifications can be considered from the following aspects:
1. Reaction type and catalyst characteristics
For catalytic reactions in fixed bed reactors, if the catalyst particles are small, in order to avoid catalyst leakage and ensure good gas or liquid distribution, you can choose a small diameter inert ceramic ball, such as 6mm-15mm. Such porcelain balls can be filled at the bottom and top of the catalyst bed to support and cover, preventing the loss of catalyst. At the same time, the smaller porcelain ball can be better matched with the catalyst, so that the fluid distribution in the bed is more uniform, improving the reaction efficiency.
If the catalyst particles are large or easy to break, it is necessary to choose a large diameter inert ceramic ball to provide stronger support. For example, for some heavy catalysts or under high pressure, high flow rate process conditions, you can consider using 25mm-50mm porcelain balls. This can reduce the risk of compression deformation and breakage of the catalyst, and extend the service life of the catalyst.
Second, equipment size and structure
In small reactors or towers, due to limited space, inert ceramic balls of smaller sizes should be selected to ensure that they can be fully filled and function. For example, for reaction tubes or experimental devices with smaller diameters, 3mm-10mm porcelain balls can be selected. These small size porcelain balls can be better adapted to narrow Spaces and are able to provide adequate support and fluid distribution effects in a small volume.
For large industrial reactors, the height, diameter and internal structure of the equipment need to be considered. In general, the larger diameter inert ceramic ball specifications are more suitable for large equipment because they provide stronger support and can reduce the height of the filling layer when filling, reducing the pressure drop. For example, in a large diameter tower, a 40mm-60mm porcelain ball can be selected as the bottom support, and then gradually use a smaller diameter porcelain ball for transition filling to achieve good fluid distribution and support effects.

Catalyst Inert Ceramic Packing Process

Is ceramic an inert waste?
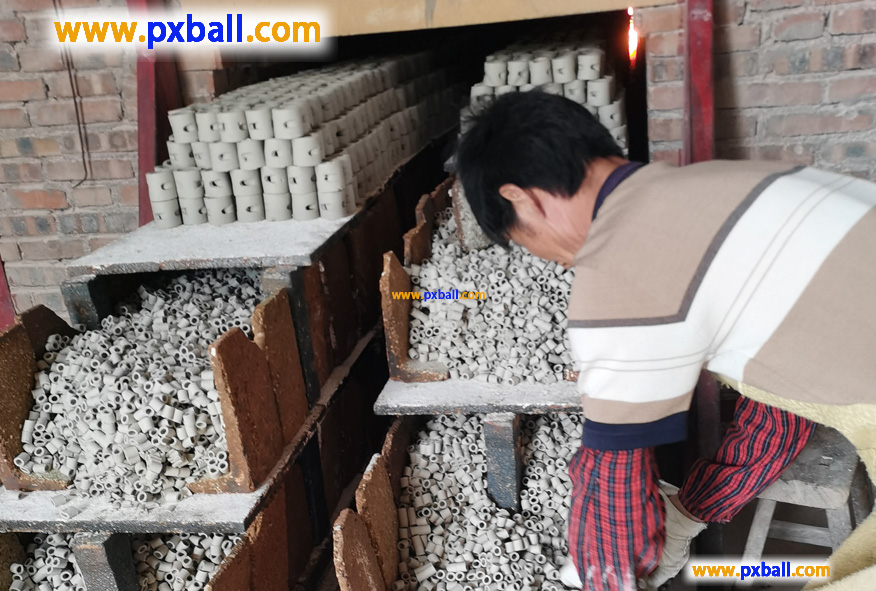

Are ceramics chemically inert?
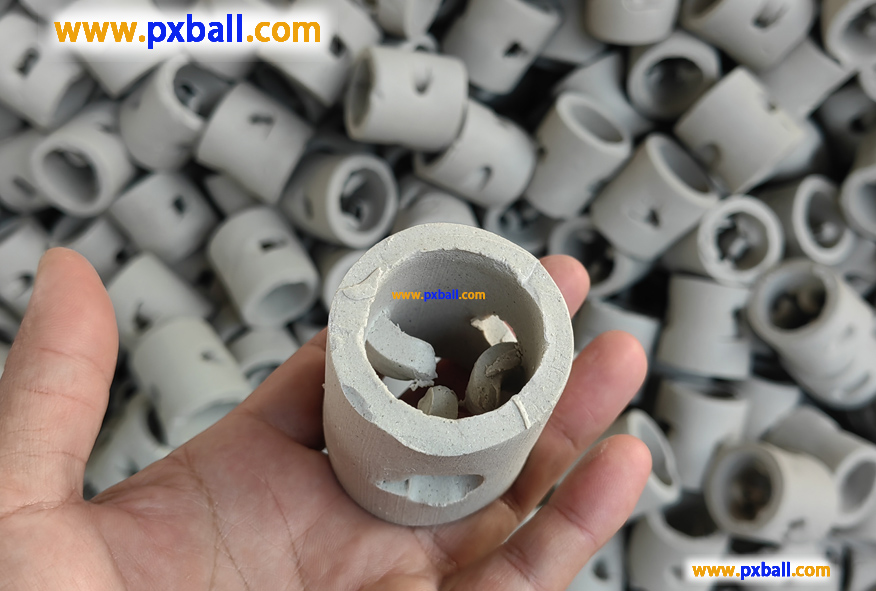

What is inert ceramics?
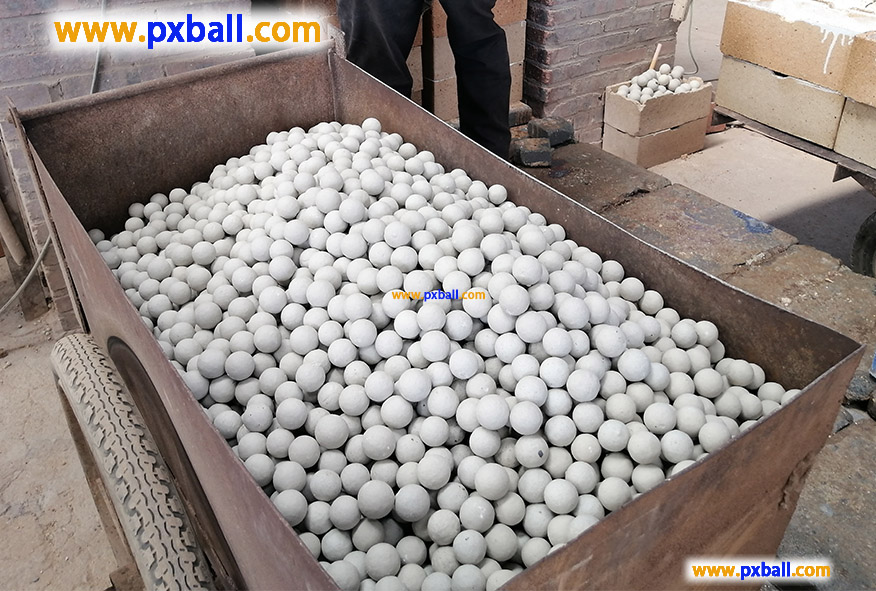

inert alumina ceramic ball density

Why do inert ceramic balls emphasize the level of aluminium content?
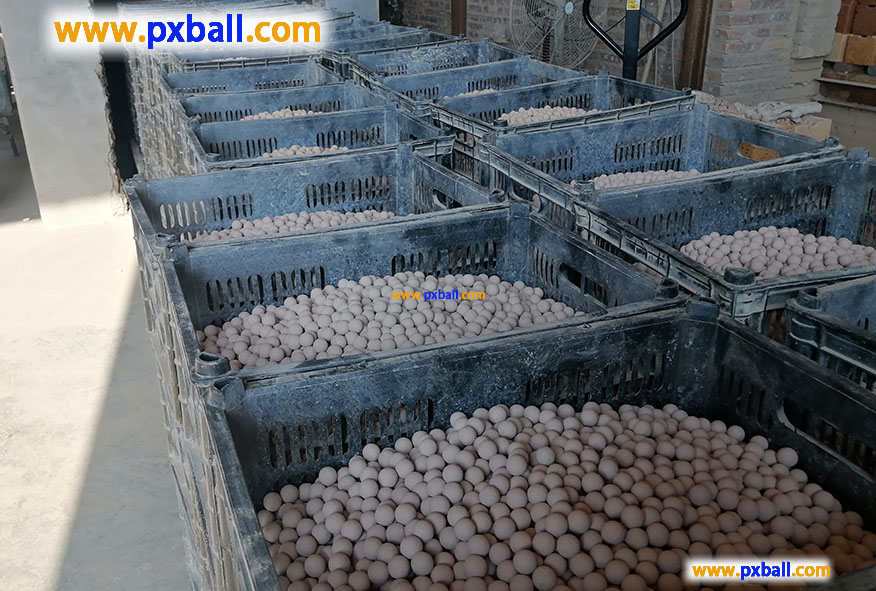

What are alumina ceramic balls used for?

What is inert ceramic ball?